Galaxy S10 wireless charger FCC: Ever wondered about the hidden tech behind that sleek wireless charging pad? We’re diving deep into the nitty-gritty of how Samsung’s Galaxy S10 wireless charger navigates the complex world of FCC regulations. From its technical specs and design to its environmental impact and troubleshooting tips, we’re spilling the beans on everything you need to know. Prepare for a wireless charging deep dive!
This exploration covers the FCC’s specific requirements for wireless chargers, how Samsung’s Galaxy S10 model measures up, and the rigorous testing involved. We’ll also compare its performance and compliance with other similar devices, giving you a comprehensive overview of this often-overlooked aspect of your tech.
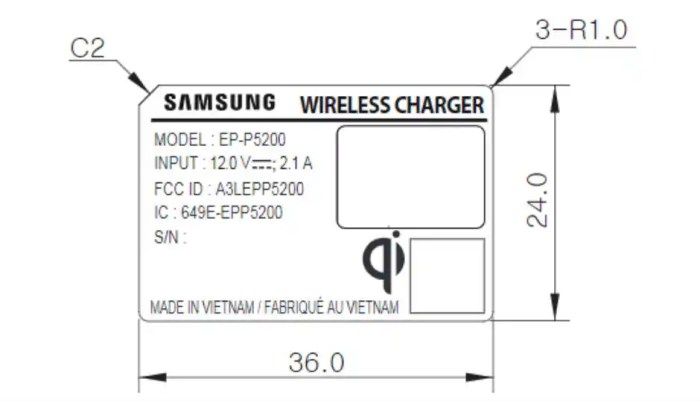
Technical Specifications and Design of the Wireless Charger: Galaxy S10 Wireless Charger Fcc
The Galaxy S10 wireless charger, while seemingly simple, is a marvel of miniaturized engineering, cleverly packing sophisticated technology into a compact and aesthetically pleasing design. Understanding its technical specifications and internal workings reveals the intricate dance of energy transfer that powers your phone without wires.
Technical Specifications
The following table summarizes the key technical specifications of the Samsung Galaxy S10 wireless charger. Note that precise specifications might vary slightly depending on the specific model and region.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Power Output (Max) | 15W (Fast Wireless Charging 2.0) |
| Input Voltage | 5V, 9V, or 12V (depending on power adapter) |
| Operating Frequency | 110-205 kHz (Qi standard) |
| Charging Efficiency | Approximately 70-80% (varies depending on factors like phone battery health and environmental temperature) |
Internal Components and Functions
The charger’s functionality relies on a coordinated interplay of several key components. At its core is a sophisticated control circuit that manages power delivery and communication with the phone. This circuit regulates the voltage and current to ensure optimal charging and prevent overheating. A high-efficiency switching power supply converts the input voltage from the wall adapter to the appropriate voltage required for wireless charging. This process is crucial for minimizing energy loss and maximizing efficiency. The charging coil, a crucial component, uses electromagnetic induction to transfer power wirelessly. This coil generates a magnetic field that interacts with a corresponding coil within the phone, inducing a current that charges the battery. Finally, various protection circuits are integrated to prevent short circuits, overcharging, and overheating, ensuring both the safety of the device and the longevity of the battery.
Energy Transfer Process Diagram
Imagine a simple diagram: A rectangular box represents the wireless charger. Inside, a circular coil is depicted, highlighted in a different color. Arrows indicate the alternating current flowing into the coil from the power supply (another box connected to the charger box). The coil generates a magnetic field, represented by concentric circles emanating from the coil. Above the charger, another rectangular box represents the Galaxy S10. Inside this box, a similar circular coil is shown. Arrows show the magnetic field lines from the charger’s coil inducing a current in the phone’s coil. Finally, an arrow leads from the phone’s coil to the phone’s battery, indicating the charging process. The entire system is enclosed within a larger rectangle representing the overall charging setup. This visual representation simplifies the complex electromagnetic interaction but captures the essence of the wireless power transfer.
Comparison with Other Wireless Charging Standards
The Galaxy S10’s wireless charging primarily utilizes the Qi standard, a widely adopted wireless power transfer technology. While Qi is a broadly accepted standard, various implementations exist, offering different power output levels and charging speeds. The Galaxy S10’s charger supports Fast Wireless Charging 2.0, which allows for faster charging speeds compared to older Qi implementations. Other proprietary wireless charging technologies exist, but Qi’s interoperability across different brands and devices is a significant advantage. The key difference often lies in the charging speed and power delivery optimization tailored for specific phone models.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The Galaxy S10 wireless charger, like all electronic devices, has an environmental footprint. Understanding its impact, from material sourcing to energy consumption, is crucial for responsible consumption and encourages the development of more sustainable alternatives. This section delves into the environmental considerations surrounding the charger’s lifecycle.
The Galaxy S10 wireless charger’s environmental impact is multifaceted, stemming primarily from its manufacturing process and operational energy use. The materials used, their sourcing, and the energy expended in production significantly contribute to its carbon footprint. Furthermore, the charger’s ongoing energy consumption during operation adds to its overall environmental impact. A comprehensive assessment necessitates examining these factors individually and collectively.
Materials and Manufacturing, Galaxy s10 wireless charger fcc
The Galaxy S10 wireless charger is composed of various materials, including plastics (likely ABS or polycarbonate), electronic components (integrated circuits, capacitors, etc.), and potentially some metals like copper for wiring. The extraction and processing of these raw materials carry environmental costs. Plastic production, for example, relies heavily on fossil fuels and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Mining for metals can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution. The manufacturing process itself involves energy consumption, often from non-renewable sources, leading to further carbon emissions. The overall environmental impact of the manufacturing process depends heavily on the sourcing of materials and the efficiency of the manufacturing facilities. For example, using recycled plastics or sourcing materials from suppliers committed to sustainable practices could significantly reduce the environmental burden.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint
The Galaxy S10 wireless charger’s energy consumption is relatively low during operation. However, even small amounts of energy consumption add up over time and across many users. The charger’s standby power consumption, while typically minimal, also contributes to its overall energy usage. To estimate the charger’s carbon footprint, one would need to consider the energy used in manufacturing, transportation, and operation, factoring in the source of that energy (renewable vs. non-renewable). For instance, if the charger is powered by a grid primarily reliant on coal, its carbon footprint would be higher than if powered by a grid with a significant renewable energy component. A detailed life cycle assessment (LCA) would provide a more precise calculation.
Improving the Environmental Friendliness of Wireless Charging
Several strategies can improve the environmental friendliness of wireless charging. Using recycled materials in manufacturing is a crucial step. Design improvements focusing on increased energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and easier repairability could also lessen the environmental burden. Encouraging users to properly dispose of the charger at the end of its life, utilizing recycling programs, is essential to prevent electronic waste from accumulating in landfills. Furthermore, promoting the use of renewable energy sources to power the charger directly reduces its carbon footprint. The development of more energy-efficient charging technologies and the use of biodegradable or recyclable materials in charger construction are also vital areas for improvement.
Comparison with Similar Products
The environmental impact of the Galaxy S10 wireless charger is comparable to other similar wireless chargers on the market. The key differences lie in the materials used, manufacturing processes, and energy efficiency. Chargers utilizing recycled materials or more energy-efficient designs would have a lower environmental impact. A direct comparison requires detailed LCAs for each product, which are not always publicly available. However, consumers can make informed choices by looking for certifications indicating sustainable manufacturing practices or energy efficiency ratings. Ultimately, responsible consumption involves considering the entire lifecycle of the product and choosing options with a demonstrably lower environmental footprint.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Let’s face it, even the sleekest tech gadgets can throw a wrench in the works sometimes. Your Galaxy S10 wireless charger, while a marvel of modern convenience, isn’t immune to the occasional hiccup. This section dives into the most common issues users encounter and provides straightforward solutions to get you back to effortlessly juicing up your phone.
Common Problems and Solutions
A quick reference guide can save you hours of frustration. This table Artikels common problems and their solutions, so you can quickly diagnose and fix the issue.
| Problem | Solution | Possible Cause | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Charging | Ensure your phone and charger are properly aligned. Check for foreign objects between them. Try a different outlet. Verify your phone’s battery health. | Misalignment, foreign objects, low power outlet, degraded battery | Regularly clean the charging surfaces. Use a high-quality power outlet. Monitor battery health. |
| Charging Failure | Check the power connection. Try a different outlet or cable (if using a wired charger adapter). Ensure both the phone and charger are clean and free from debris. Check for software updates on your phone. | Power outage, faulty cable, debris, software glitches | Keep the charging surfaces clean. Use a surge protector. Regularly update your phone’s software. |
| Overheating | Remove your phone case. Ensure proper ventilation around the charger. Allow the charger and phone to cool before resuming charging. | Poor ventilation, thick phone case, high ambient temperature | Use a thin phone case or remove it during charging. Ensure adequate airflow. Avoid charging in direct sunlight or high temperatures. |
| Intermittent Charging | Try repositioning your phone. Clean both the phone and charger surfaces. Check for any damage to the charging coil. | Misalignment, debris, damaged charging coil | Keep the charging surfaces clean. Handle the charger with care to avoid damage. |
Troubleshooting Slow Charging or Charging Failures
Let’s tackle those frustrating slow charging or complete charging failures head-on. First, the basics: confirm the charger is plugged into a working outlet. Try a different outlet to rule out power issues. Next, meticulously clean both the charging surfaces on your phone and the wireless charger itself. Even tiny specks of dust or lint can disrupt the connection. If you’re using a phone case, remove it – bulky cases can interfere with charging efficiency. If the problem persists, check your phone’s battery health; a degraded battery may charge more slowly. Finally, ensure your phone’s software is up-to-date, as software bugs can sometimes impact charging performance.
Preventative Measures
Preventing problems is always easier than fixing them. Here’s how to keep your Galaxy S10 wireless charger running smoothly: Keep the charging surfaces clean – a microfiber cloth works wonders. Avoid charging your phone in extreme temperatures or direct sunlight. Use a thin phone case or remove it during charging to improve ventilation. Regularly check your phone’s battery health and consider a replacement if it’s significantly degraded. And finally, keep your phone’s software updated to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements.
Repair or Replacement Options
If, despite your best efforts, your wireless charger still malfunctions, you have a couple of options. Depending on the nature of the problem and whether it’s still under warranty, you might be able to get it repaired through Samsung’s service centers. If repair isn’t feasible or cost-effective, replacing the charger is the next step. Consider purchasing a certified Samsung replacement to ensure compatibility and quality. Always check online reviews before buying a replacement charger from third-party sellers.
So, there you have it – the inside scoop on the Galaxy S10 wireless charger and its journey through the FCC gauntlet. From understanding the intricate technical specifications and safety features to addressing common problems and considering its environmental footprint, we’ve covered the spectrum. Remember, understanding your tech isn’t just about using it; it’s about appreciating the engineering and regulatory hurdles it overcomes to power your devices conveniently and safely.
 Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru
Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru