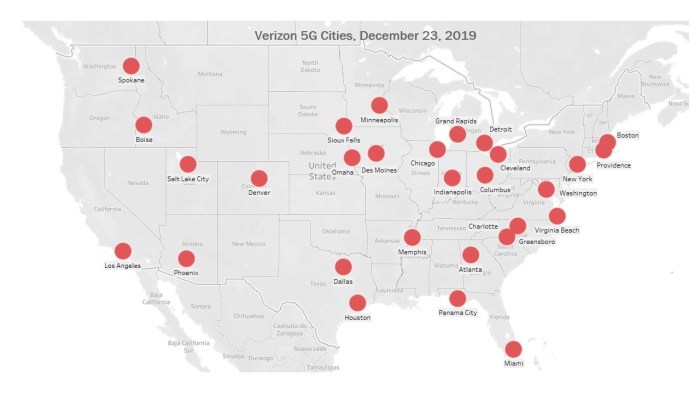
Verizon 5G network deployed 30 cities 2019 – remember that? It was a huge moment for the telecom giant, a bold step into the future of connectivity. This wasn’t just about slapping 5G onto existing infrastructure; it was a strategic play, a gamble on a new technology in a rapidly evolving market. We’ll dive into the rollout, the tech behind it, the marketing blitz, and the early user reactions, painting a picture of Verizon’s 2019 5G gamble.
From city selection to the challenges of deploying cutting-edge technology in diverse urban environments, we’ll explore every aspect of this pivotal moment in mobile history. We’ll also compare Verizon’s approach to its competitors, highlighting the strategic differences and the competitive landscape that emerged.
Early User Experiences and Feedback: Verizon 5g Network Deployed 30 Cities 2019
Verizon’s 2019 5G rollout, initially spanning 30 cities, marked a pivotal moment in the mobile landscape. The early adopter experience, a blend of excitement and frustration, shaped both consumer perception and the future trajectory of 5G development. This section explores the initial user feedback, its impact on Verizon’s brand, and the limited range of devices available at the time.
The launch wasn’t without its hiccups. Early 5G experiences were a mixed bag, reflecting the nascent stage of the technology and the challenges of widespread deployment. While some users raved about the speed, others faced connectivity issues and limitations.
Positive and Negative User Experiences, Verizon 5g network deployed 30 cities 2019
Early user reviews painted a picture of both the promise and the limitations of Verizon’s initial 5G network. Positive experiences centered around speed and performance in ideal conditions, while negative experiences highlighted coverage gaps and inconsistent performance.
- Positive Experiences: Many users reported significantly faster download and upload speeds compared to 4G LTE, particularly in areas with strong 5G signal. This translated to quicker streaming, smoother online gaming, and faster file transfers. Some users also noted improved latency, resulting in a more responsive online experience.
- Negative Experiences: A common complaint was limited 5G coverage. The network’s reach was often patchy, with users experiencing frequent drops back to 4G LTE, even in cities where 5G was supposedly available. Another significant issue was the high cost of 5G plans and the limited number of compatible devices initially available.
Impact on Verizon’s Brand Perception
The initial 5G rollout significantly impacted Verizon’s brand perception. While the promise of blazing-fast speeds generated considerable buzz and excitement, the inconsistent performance and limited coverage led to some disappointment and skepticism among consumers. This initial mixed reception highlighted the challenges of launching a new, complex technology on a large scale. While Verizon maintained its reputation as a major player in the telecommunications industry, the early 5G experience served as a reminder that technological advancements often come with growing pains.
Available 5G Devices at Launch
The selection of 5G devices at the initial launch was severely limited. This constraint further impacted the early user experience, as many consumers were unable to access the new network immediately. The few available devices often came with their own set of limitations.
- Motorola Moto Z3 with 5G Moto Mod: This was one of the first commercially available 5G devices. It relied on a modular add-on (the Moto Mod) to provide 5G connectivity, making it bulky and less elegant than fully integrated 5G phones. Battery life was also a concern for some users.
- Samsung Galaxy S10 5G: Samsung’s flagship 5G phone offered a more integrated 5G experience compared to the Moto Z3. However, it was initially priced at a premium, limiting accessibility for many consumers. Its large screen size and battery capacity also contributed to its larger form factor.
- Other Early Adopters: A few other devices, including some from LG and others, began appearing as the year progressed. These also faced similar limitations in terms of availability, price, and battery life, often reflecting the early stages of 5G technology development.
Comparison with Competitors’ 5G Rollouts (2019)
In 2019, the 5G race was on, and Verizon’s launch in 30 cities marked a significant step. However, understanding Verizon’s position requires looking at how its competitors, AT&T and T-Mobile, approached the early 5G deployment. Each company adopted a distinct strategy, reflecting differing technological choices and market priorities.
The contrasting approaches resulted in a diverse competitive landscape, with each carrier targeting different segments of the market and emphasizing specific aspects of 5G technology. This created a dynamic situation where consumers benefited from a variety of options, but also faced the challenge of understanding the nuances of each network’s capabilities.
Competitive 5G Deployment Strategies in 2019
| Company | Number of Cities (Approximate) | Deployment Technology | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verizon | 30 | mmWave (high-band) | Early adopters, dense urban areas |
| AT&T | More than Verizon, but with lower speed initially | Mix of mmWave and low-band | Broader coverage, gradual rollout |
| T-Mobile | Significant number of cities, broader coverage | Low-band (600 MHz) | Wider geographic reach, nationwide coverage |
The table above illustrates the key differences in the three carriers’ strategies. Verizon initially focused on mmWave technology, offering incredibly fast speeds but with limited range and coverage. This approach targeted early adopters in dense urban areas where mmWave’s high capacity was most beneficial. AT&T adopted a more balanced approach, utilizing both mmWave and lower-band spectrum to achieve a mix of speed and coverage. T-Mobile, on the other hand, prioritized nationwide coverage using its existing low-band spectrum, providing a wider reach but at the cost of lower peak speeds.
Key Differences in Approach
The core difference lay in the chosen spectrum and the resulting trade-off between speed and coverage. Verizon’s mmWave bet was a high-risk, high-reward strategy. While delivering blazing-fast speeds, it suffered from significant coverage limitations. AT&T attempted to strike a balance, but this dual approach meant neither speed nor coverage significantly outperformed the others. T-Mobile’s low-band strategy prioritized accessibility and widespread availability, positioning it as a more readily available option for the average consumer.
Competitive Landscape of the 5G Market in 2019
The 2019 5G landscape was characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and experimentation. Verizon’s aggressive, albeit limited, mmWave rollout represented a bold bet on the future of 5G. AT&T’s more cautious approach reflected a desire to balance immediate market penetration with long-term network investment. T-Mobile’s emphasis on low-band coverage positioned it as a more accessible option for the mass market. This diverse approach created a competitive environment where each carrier emphasized different aspects of 5G, offering consumers a range of choices based on their priorities.
Verizon’s 2019 5G launch in 30 cities wasn’t just a technological feat; it was a strategic maneuver in a burgeoning market. The rollout, while ambitious, revealed the complexities of deploying a new generation of wireless technology. By analyzing the successes and challenges, we gain valuable insights into the evolution of 5G and the ongoing race for mobile supremacy. The early days of 5G were filled with both excitement and uncertainty – a perfect storm of innovation and anticipation that shaped the landscape of wireless connectivity as we know it today.
 Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru
Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru